Contents
If you’re here to learn about blockchain technology, I can presumably say you might’ve heard of bitcoins. Those are among the most hyped use cases of blockchain. Even if you aren’t aware, we all exchange values in our day-to-day lives, and blockchain can revolutionize how we trust each other in an economy. It can change our fundamental patterns of risking our trust to relying on a community for infallible information and attested transactions.
What is Blockchain?
Ever bought a real estate property from someone? You’re always bound to trust the seller that they’ll provide you with all the necessary correct information. They have the authority to manage the data inside the mother deed, and you wouldn’t know if they tamper with it to sell land that might even be illegal. How are you supposed to ensure that you get all the vital information in that case?
In its simplified intent, blockchain is a database technology that helps decentralize this power among a network and each actor involved in this network acts as a miner to verify every piece of information being added to the chain.
In technical terms, a blockchain is a digitally distributed, persistent, transparent, public, append-only ledger. It is a system to which data can be added but once entered, it is immutable. Data can be added through a mechanism of creating a consensus of 51% (at least) among all the parties connected over the network.
How does the Blockchain work?
Similar to, how in an excel sheet data is structured into cells, in a blockchain information is structured in the form of blocks. These blocks are made of 3 main elements:
- Data (information stored in that block)
- Hash (a fingerprint of that block to uniquely identify it)
- Hash of previous block (to form a chain of blocks)
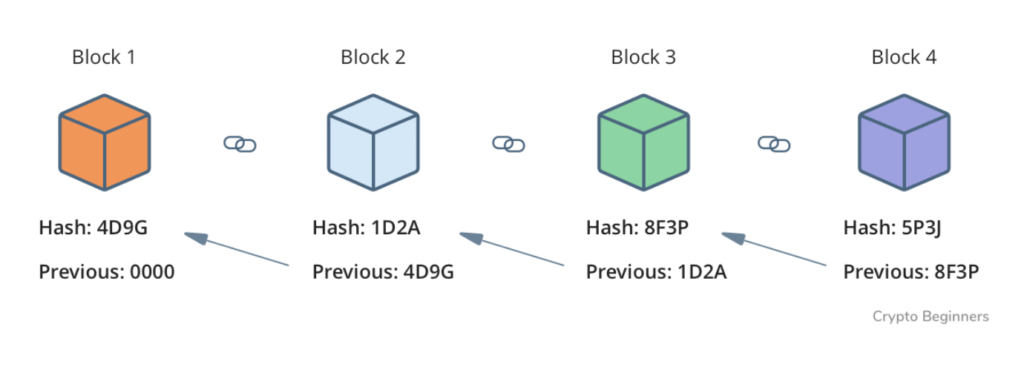
What makes blockchain secure is that if you try to tamper with the data of any block, the hash of that block will change, causing changes in the hash of the following blocks and eventually leading the chain to crash. This makes it easier to trace the problem to its source.
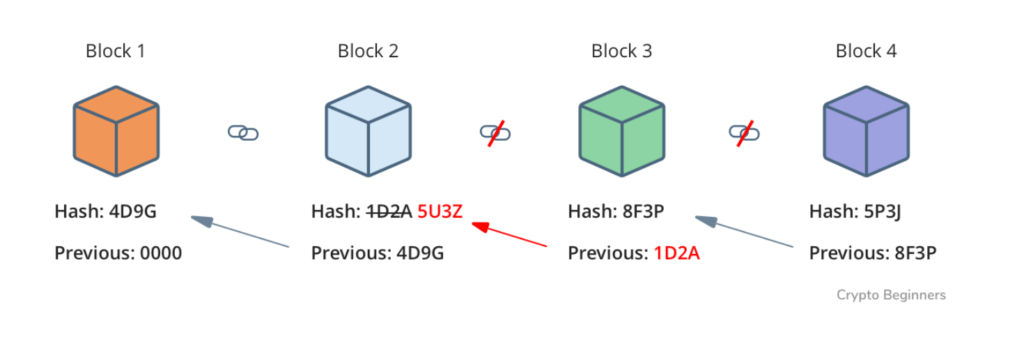
The second major reason for Blockchains being secure is the decentralization of the data.
Blockchain is stored and run by a network of computers collectively. Whenever new data is added to the blockchain, it’s the work of the people on the network to verify, whether the person adding the data has done anything to tamper with the information or not.
It ensures that no individual actor on the network can force the blockchain to accept a particular entry onto the ledger that others disagree with.
It forms a peer-to-peer network that can maintain updates to the database and then verify them in a way making it impossible to defraud and alter after.
Types of Blockchain
Public Blockchain:
Public blockchains are open to all. Anyone interested in joining the network can participate and act as a merchant, a buyer, a minor, a developer, or even just a community member. These are 100% decentralized with no private ownership. All transactions are transparent and visible to people outside the network too.
Private Blockchain:
Private blockchains are mostly used by large companies that wish to have more control over the network. Participants can have different levels of limited access decided by the authority. These are operated in an isolated environment, are much smaller and every participant can be identified, unlike public blockchains where anonymous transactions are permitted. Private blockchains are faster and comparatively more centralized. When governed by a group rather than a single entity, these are referred to as consortium blockchains.
Hybrid Blockchain:
As the name suggests, hybrid blockchains lie somewhere between private and public blockchains. They are a combination of public as well as private data. Mostly brought in use to limit the disadvantages of the extreme types and optimize the functionality.
Why is it important to learn about this?
Blockchain is a revolutionary technique to fill in the trust gap which in today’s world is being handled by intermediaries. It has the potential to remove third-party interferences in all the transactions that we face in daily life.
We have all witnessed the hype around Bitcoins and cryptocurrencies and how blockchains have been used for banking and payment purposes but there’s more to blockchain’s implementation in today’s world.
- Education boards can use blockchain to directly upload all educational records securely, accurately, and easily accessible when in need.
- In the healthcare industry, medical records can be securely hosted over a blockchain network so that the information is easily accessible by approved parties and can not be tampered with.
- Implementing accurate and secure voting without relying on a third party like Election Commission and guaranteeing legitimate elections throughout the country.
And yet, we only are in its initial stages and there’s so much more to learn about this revolutionary idea. An idea to transform from a world living in a data monarchy to a data democracy.

