Contents
The main motto of this project is to develop a low-cost, high-performance satellite bus and requisite customer ground transceivers to implement a new spaceborne Internet communication system. So in this article let’s know the impact of Starlink project on human life.
What is Starlink?
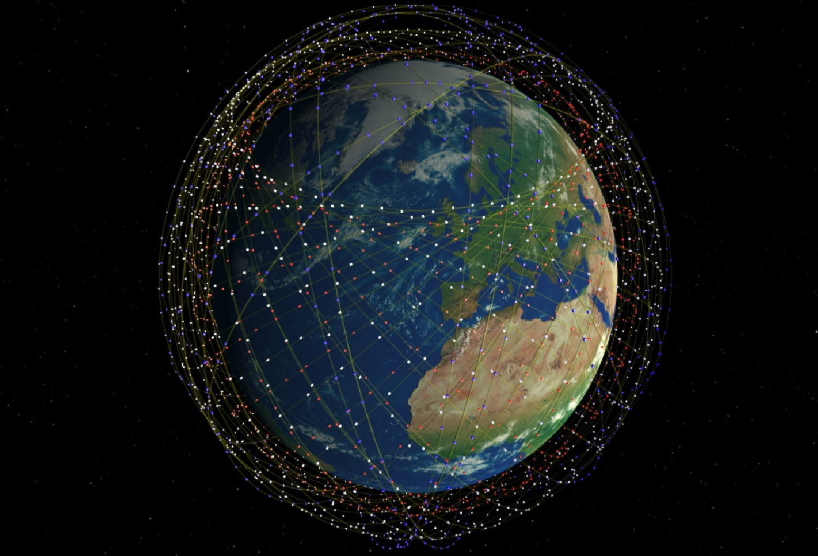
Starlink is a satellite constellation being constructed by SpaceX to provide satellite Internet access. Constellation means a group of stars forming a recognizable pattern. The constellation will consist of thousands of mass-produced small satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO). Working in combination with ground transceivers. Know all you need to know about SpaceX’s Starlink Project.
SpaceX has said it will offer speeds up to 1 Gbit/s, with latencies between 25 ms and 35 ms. Latency is the delay that occurs in receiving and sending data packets to the server and client. Those latencies would make SpaceX’s service comparable to cable and fiber. While existing satellite broadband services have latencies of 600 ms or more, according to FCC measurements.
Main Aim of Starlink :
Satellites are used for communication since the 1960s ,Space-based internet is not a new idea . These communication satellites are typically located in a geostationary orbit, which has advantages and disadvantages. Since the satellite is in geostationary orbit, this means it always appears in the same place in the sky from Earth. Here, the receiving antenna doesn’t need to track the satellite.
Unfortunately, a geostationary orbit is a long way above the Earth, meaning it isn’t a quick journey for even light to make. Signals are weak by the time they are received. This limits the speed of traditional internet satellites to an average of around 1 Mb/s for downloads, 256 kB/s for uploads, and latency of over 600 ms. This is slower than a traditional broadband connection, with a latency around 10x higher as well. These factors combined give limited use, and make them unsuitable for most uses, as well as being very costly.
SpaceX aims to avoid these problems by bringing their satellites closer to the Earth. While geostationary satellites are over 35,000 km away. Some of the Starlink constellations will be only 340 km above the Earth.
Benefits of this Project :
- The problems with speed and latency will disappear when you bring the satellites closer.
- Individual Starlink’s will be traveling at nearly 30,000 km/h and not very high up. This means each one will only be able to see a small amount of the Earth for a short time as it zooms on by.
- The receivers on Earth also need to be able to track the fast-moving satellites. Though this can be done by steering a beam rather than having to mechanically move the receiver dish.
What’s good about Starlink:
1) Global Access:
Access to high-speed internet will be possible for the first time in rural, isolated, and developing areas. At the moment around 1% of African people have access to broadband internet. With a Starlink antenna, high-speed internet will be a click away, anywhere on Earth.
2) Faster:
Starlink will be faster than the undersea fiber-optic cables that carry internet traffic worldwide today. This is because signals are traveling at the speed of light. About 50% faster than it can travel through a fiber optic cable.
What’s adverse about Starlink?
There will always be a Starlink satellite in view, almost anywhere in the world.
Starlink needs a lot of satellites, and that causes problems for astronomers. As the satellites travel around, they run the risk of getting in the way of objects astronomers are interested in looking at.
The visibility of the satellites also depends on the local time and whether or not the satellites are illuminated. Which only occurs around sunrise and sunset, times not generally well suited to doing astronomical observations. To minimize these effects, the satellites can be painted to limit how reflective they are, and astronomers can check when a Starlink satellite will pass overhead.
While communicating with users on Earth using radio waves, the signals from the satellites may get in the way of astronomers studying the sky at these wavelengths. Unfortunately, this cannot be solved with simple paint, and concerns have been raised about the future of radio astronomy .
The “mesh” of the Starlink net is big enough that we can still easily launch into space through the holes in the net. But there are concerns that the mesh may not always be so wide.
So many objects in orbit traveling at 30,000 km/h, if any collide the resulting crash would be catastrophic. Debris traveling faster than a rifle bullet will form a new net around the Earth with a tighter mesh, threatening to strike other satellites, generates more debris. Before long this runaway effect, called Kesler syndrome, could create such a tight net around the Earth . It will be even trickier and more dangerous to launch into space than it is now.
There are already over 10,000 pieces of space junk in orbit, As we put more and more objects into space, the chances of a collision increase. While Starlink is capable of autonomous collision avoidance, it has to know what it is avoiding.
Is Starlink Good or Bad?
Starlink has the potential to connect people who don’t have internet access. It promises high speed, low-cost internet access to everyone, wherever they may be.
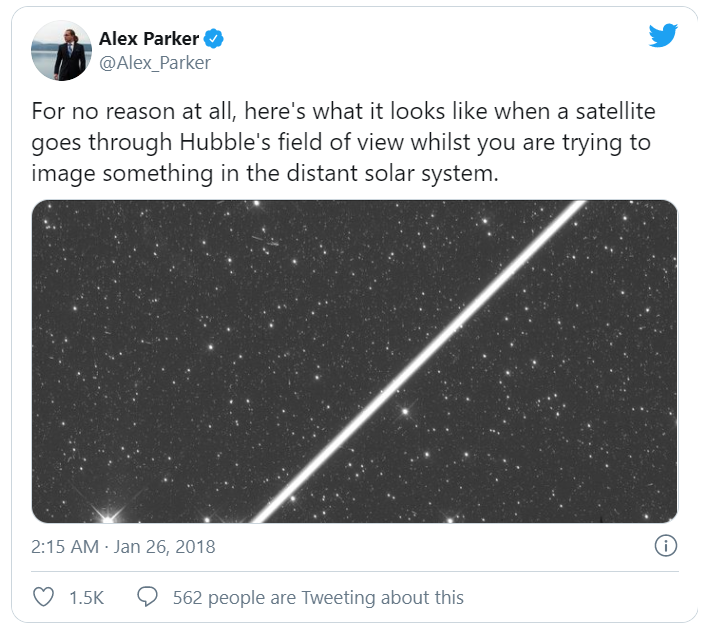
The problem is there is very little public data on how such giant constellations could pollute the night sky with light. The discussion of light pollution exploded over the weekend after amateur astronomers released footage of the Starlink satellites. Showing them to be much brighter than people imagined.
One astronomer, Cees Bassa, attempted to do the math and calculated just how many of these satellites might be visible in the sky at one time. For his analysis, he factored in the first leg of SpaceX’s Starlink constellation – about 1,600 satellites . As there are better details about the orbits they’re going to. Based on just that initial batch, he estimated that at a latitude of 52 degrees north (about where London is located), there will be 84 Starlink satellites above the horizon at all times. And for many hours around dusk, dawn, and in the nighttime during summer, 15 of those satellites would be visible in the sky at all times, about 30 degrees above the horizon. Of course, that’s just the first batch of Starlink satellites, the impact of additional spacecraft could be worse.
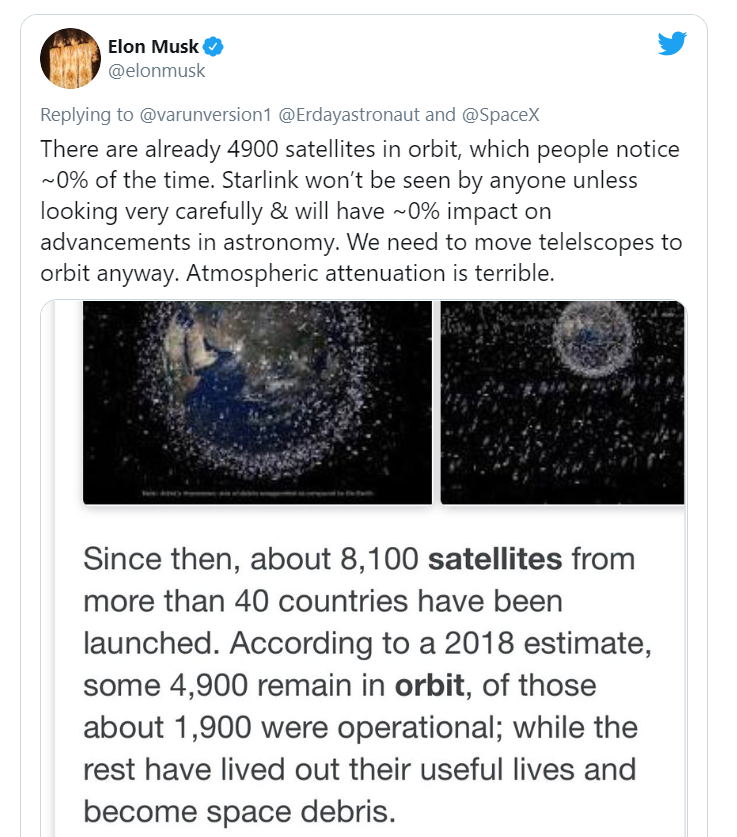
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk tried to downplay the astronomy community’s concerns, arguing that Starlink would have “~0% impact on advancements in astronomy”. He also claimed that the satellites would not be visible when the stars are out. And that’s the reason the International Space Station is visible at night is that it’s big and has lights — two statements that aren’t true.
According to many astronomers. Telescopes can be built much bigger on Earth with dishes more than 30 meters (98 feet) in diameter.Allowing astronomers to take in a lot of light and get more detailed observations. Launching such a massive telescope off of Earth is incredibly difficult, requiring giant rockets or very complex engineering.
The good news is that the current batch of Starlink satellites are already getting dimmer. They are slowly moving to their final higher orbits and spreading far apart.
But it’s not just light that astronomers are worried about. Some are concerned that the radio frequencies these satellites will be transmitting on will also interfere with radio observations of the Universe. Often, astronomers will study radio waves coming from distant objects . To learn more about them, especially hot bodies like stars that emit super intense X-rays that can be measured from Earth. Musk did say that SpaceX’s Starlink satellites won’t transmit at certain frequencies to avoid astronomy observations . But it could still create a blind spot.
CONCLUSION:
Whether or not surrounding our planet with tens of thousands of satellites is a good thing remains to be seen. Constellations have the power to bring humanity together, but also trap it. The fears of the astronomy community are valid and it’s only cooperation between parties that will determine the path forwards.
Next Reads:
Starlink Project of SpaceX – All You Need To Know

My name is Vemula Chandana. I am from Hyderabad , and currently pursuing my BTech degree in Electronics and Communication Engineering in Anurag University.

Commercial airlines are much bigger and the number of fight paths are stagering at a very low orbit…but it doesn’t interfered with astronomers for ages, why should spacex be a big concern?
And it’s helps humanity to be connected even closer…Don’t get it!
Take it slow, and a little steady. Conception is in a moment, but it takes nine months for the baby to be born. Rome was not built in a day. Stop sticking that light in my eyes youngins no i’m not a sort of alien. A gentleman.